Editor's Note: This is the second and final part of a roundtable series with the three panelists. Part one was published in August 2019.
For the last several years, NACE International and the NACE International Institute have committed to researching, determining, and supporting best corrosion management practices throughout organizations to ensure safer, long-lasting protection of assets such as pipelines; increase return on investment (ROI) while decreasing life cycle costs; and preserving the environment.
To explain the value of corrosion management systems (CMS), how they work, and what programs and platforms are available to help organizations improve their corrosion control programs, three experts in oil and gas pipeline corrosion management spoke with NACE to share their knowledge and experience with CMS. They are Michael Ames, Chapman Engineering; Gerry Koch, DNV GL; and David Kroon, Aegion Corporation.
NACE: What tools do you find of value when implementing a CMS throughout an organization?
David Kroon (DK): Support of the CMS throughout the organization from executive management to field operations is most important.
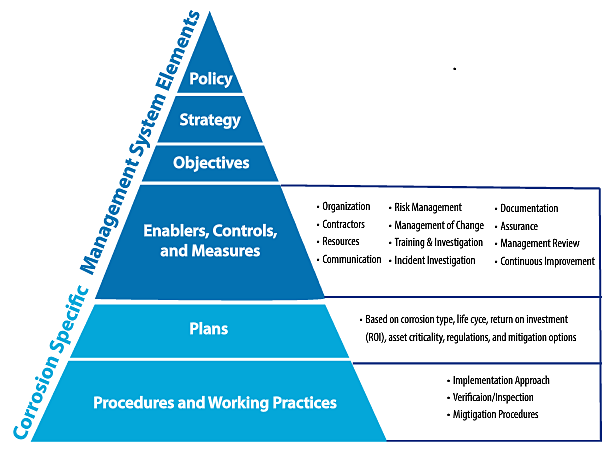
We need to invest in advancing corrosion control technology and systems, but we also need to incorporate these practices in a CMS to maximize the business benefits. This can be accomplished by employing a CMS that is understood and supported by every level of an organization involved in protecting assets. A CMS consists of the following:
• Procedures and working practices
• Plans based upon desired asset life and available mitigation measures
• Enablers, controls, and performance metrics
• Objectives, strategies, and policy
The relationship of these elements is illustrated by the CMS Pyramid (Figure 1).
I really like this figure since it does such a good job of summarizing everything needed to successfully implement a CMS throughout an organization. Our engineering groups are very good at addressing the bottom two layers of the pyramid focused on procedures and practices, and even planning for regulatory compliance, process improvements, and capital projects.
As we move toward the top of the pyramid, the need for management to be fully engaged is essential for putting in place enablers, controls, and performance measures. Executive management needs to drive the development of CMS objectives, strategy, and policy, and also needs to regularly communicate the importance of the CMS to the organization.
Gerry Koch (GK): As stated previously, a culture focused on corrosion management, much like process safety management, must exist within the organization, such that corrosion management is part of the organization’s overall management system. For this to happen there must be buy-in across the organization. First the corrosion professional should broaden his competence with respect to business tools, to include financial decision making, and risk assessment, which is based on expected activity for evaluating corrosion control expenditures. Whenever possible, Life Cycle Costing (LCC) should be considered. Financial tools exist that are described in the NACE IMPACT Study include LCC, Constraint Optimization, and Maintenance Optimization.
NACE Task Group (TG) 564 has developed a standard practice, “Standard Framework for Establishing Corrosion Management Systems,” soon to be published, which is based on a proposed framework developed in the IMPACT Study and ISO-55000 management standards. This standard practice is providing guidelines to organizations wishing to develop a CMS.
Michael Ames (MA): Some very good guidance information is available from pipeline regulatory groups such as PHMSA and B31; other great information and guidance are available within the NACE IMPACT PLUS system. There are several companies set up to “Navigate” an operating company through their existing CMS to enhance it and integrate it within all parts of the company.
NACE: What training is typically needed?
DK: Much of the needed training can be obtained through NACE. Participation in the NACE TG 564 is a good place to start. The IMPACT PLUS portal is another great resource that is accessible online. It is designed to provide a CMS framework that incorporates both technical and business considerations, including process classification frameworks, maturity models, and benchmarking. Specific tools for developing a comprehensive CMS are provided, such as a customized Corrosion Management Process Classification Framework, CMMM, and an extensive reference library. The value of IMPACT PLUS for corrosion and management professionals includes:
• An integrated platform for corrosion management professionals seeking to move their organizations to a higher level of performance
• A common language and structure needed to ensure communication throughout all levels of an organization
• A straightforward way for companies to identify gaps in processes that could lead to reduced asset life
• A model that creates a roadmap of activities, investments, and best practices
NACE International also offers a host of technical training courses and certification programs including CP, protective coatings, pipeline integrity, and marine corrosion control.
GK: With the support of the new NACE standard practice, organizations can start to develop their CMS strategies. The NACE IMPACT PLUS CMS tool can assess where an organization stands with respect to corrosion management and through “Aspiration” workshops to develop a roadmap where the organization needs to go to meet CMS requirements that fit the specific organization.
MA: Training to use CMS programs is usually self-taught or from a company’s internal training program. These programs are enhanced by attending industry pipeline safety and corrosion control seminars around the world. Specific to enhancing their use and maturity, the IMPACT PLUS Navigator training program would be the best in my experience to recommend.
NACE: In your experience, how extensively are CMS programs being used in the corrosion industry today? How can their use be more prevalent?
DK: CMS means different things to different people and organizations. In its simplest form for the regulated pipeline industry, it means nothing more than a program to ensure continuing compliance with PHMSA and EPA corrosion control regulations. This is a short-sighted approach since it robs the organization of all the other benefits. I maintain that a good regulation is good for industry, but we need to work at reaping the benefits. Corrosion engineers regularly speak to management in the terminology of their science and technology. They need to adopt the language of their management and regularly expand the conversation to include discussions of safety, ROI, and LCC. Corrosion threats should be mitigated to a point where the expenditure of resources is measured against the benefits gained. To determine whether a corrosion management investment is appropriate, it can be compared to the potential corrosion consequence through an ROI analysis, which often includes inspection and other maintenance costs.

MA: My experience has been involved with the coverage and separation between CMS and pipeline integrity groups that tend to be somewhat at arms-length, when really, they do overlap and can enhance each other more than some have at this time. The significance of this relationship is that one group has a more enhanced corrosion management practice than the other. To fully integrate these practices in appropriate situations is needing more attention, in my opinion. CMS should be understood and observed in all areas of a company, as they all have their contribution to make to enhance pipeline corrosion management. Consider the impact of budgeting, construction practices, and operation processes—they all impact the ability of a company to manage corrosion, but in many setups, they do not know their involvement or impact. The use of a CMS must be enhanced by having each group understand their part to play and would usually require meetings to discuss how they interlock with the CMS.
GK: The concept of corrosion management may often mean different things to different people and organizations. While over the past few years the understanding of what corrosion management is has increased, there is still a long way to go, since a considerable number of people and organizations regard the concept of corrosion management to be similar to or the same as corrosion engineering. For example, in the pipeline industry corrosion management often means simply meeting regulatory requirements by carrying out CP and internal corrosion monitoring programs. These programs are considered a cost to the bottom line and corrosion professionals have to constantly justify these costs, while no consideration is given to cost benefits and ROI. These organizations can broaden their view of corrosion management by considering the economic impact of implementing corrosion engineering versus not implementing. By developing a culture of corrosion management through buy-in throughout the organization, the full benefit of corrosion management can be achieved.
The corrosion management concept as envisioned by NACE and the co-contributors to this article is embraced by some oil and gas companies, which have started to create a corporate culture with buy-in from all levels of management, where corrosion is being part of the companies’ overall management system.
NACE: Please share any additional comments you may have.
MA: Pipeline CMS are the first and best line of protection from corrosion of a pipeline asset. As these programs mature across companies, and the world, there should be a better assurance that a pipeline’s neighbor should never have to worry about pipeline safety.
GK: The acceptance of the CMS concept may be likened to the acceptance of today’s safety management culture. A few decades ago, safety management merely dealt with occupational safety, which considers relatively high occurrences of slips, trips, and falls, whereas process safety (low likelihood of occurrence and high consequence) received little attention. After a few major process safety-related accidents, a culture developed throughout the oil and gas and refining and petrochemical industries, where safety has become an integral part of the organizations’ management systems. All levels of the organizations now speak the same safety language and have the same goal to improve both occupational and process safety. It is my hope that corrosion will go through the same transition and become part of organizations’ corporate cultures.
DK: We have come a long way. It’s not too long ago when corrosion was viewed as inevitable—pipelines needed to be replaced because they wore out. It is now recognized by the oil and gas pipeline industry that corrosion management saves money and reduces risk. It’s just good business and the right thing to do.
Part one of this two-part series with the three panelists was published in August 2019.